Infrared Technology
Fundamental Principles of Infrared Radiation
To understand aerial thermography, it's essential to start with the basics of infrared (IR) radiation. Infrared radiation is a part of the electromagnetic spectrum, which lies just beyond the visible light range. Every object emits infrared radiation as heat, with the amount of radiation increasing with temperature. This emitted radiation is invisible to the human eye but can be detected and measured by specialized equipment.
Infrared Cameras and Thermography
Infrared cameras, central to thermography, are designed to detect and measure the infrared radiation emitted by objects. These cameras translate the radiation into electrical signals, which are then processed to form a thermal image or thermogram. This image represents the temperature distribution of the surveyed area, with different colors indicating different temperatures. Warmer areas are typically shown in reds and yellows, while cooler areas appear in blues and greens.
Integration with Aerial Platforms
Solar Shade Structure
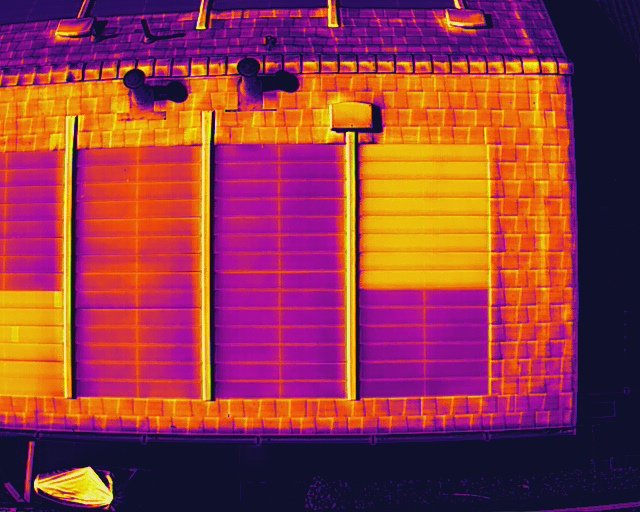
IR Image of building Facade
Residential Solar array
Broken Solar mount
Aerial thermography involves mounting these infrared cameras on aerial platforms, such as drones or aircraft. These platforms provide a vantage point for capturing wide-area thermal images from above, which is particularly useful for inspecting large or inaccessible areas. The mobility of aerial platforms allows for rapid, comprehensive coverage, making it possible to gather thermal data over large expanses quickly.
Application of Aerial Thermography in Inspections
In various inspection scenarios such as solar panels, roofs, or electrical infrastructure, aerial thermography using drones equipped with infrared cameras has proven to be highly effective. The unique perspective provided by aerial thermography offers significant advantages for identifying and addressing potential issues.
Data Processing and Analysis
The thermal data captured by the infrared cameras undergoes thorough processing using specialized software. This processing interprets the data to create detailed images that reveal temperature anomalies which are indicative of potential problems. This allows for the accurate identification of defects or issues, such as defective solar panels, heat loss in roofs, and overheating components in electrical infrastructure.
Advantages of Aerial Thermography
The synergy of aerial platforms and infrared imaging offers notable benefits:
Extensive Coverage: Enables swift inspection of large areas within a short timeframe.
High Precision: Capable of detecting subtle temperature differences that may signal potential issues, ensuring thorough inspection.
Accessibility: Facilitates the inspection of challenging or remote areas without the need for physical presence, thereby increasing safety and efficiency.
Non-invasive Inspection: Provides a non-disruptive means of inspection, minimizing any impact on the infrastructure being assessed.
Conclusion
Aerial thermography effectively amalgamates the science of infrared imaging with the advantages of aerial surveying. This technology not only enhances the efficiency and accuracy of inspections but also exemplifies the innovative application of scientific principles in practical scenarios. By aiding preventive maintenance and safety, aerial thermography stands as a testament to the capability of advanced technology in revolutionizing inspection methodologies across diverse industries.